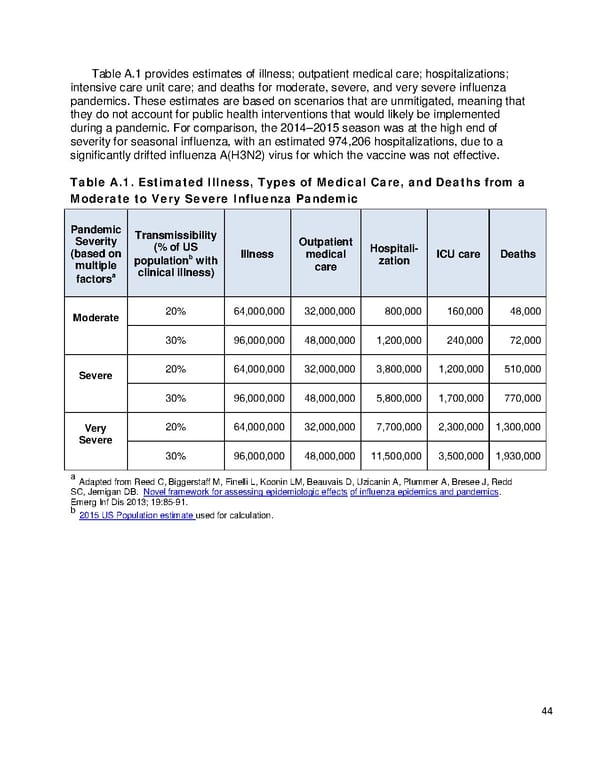
Table A.1 provides estimates of illness; outpatient medical care; hospitalizations; intensive care unit care; and deaths for moderate, severe, and very severe influenza pandemics. These estimates are based on scenarios that are unmitigated, meaning that they do not account for public health interventions that would likely be implemented during a pandemic. For comparison, the 2014–2015 season was at the high end of severity for seasonal influenza, with an estimated 974,206 hospitalizations, due to a significantly drifted influenza A(H3N2) virus for which the vaccine was not effective. Table A.1. Estimated Illness, Types of Medical Care, and Deaths from a Moderate to Very Severe Influenza Pandemic Pandemic Transmissibility Severity (% of US Outpatient Hospitali- (based on populationb with Illness medical zation ICU care Deaths multiple clinical illness) care a factors 20% 64,000,000 32,000,000 800,000 160,000 48,000 Moderate 30% 96,000,000 48,000,000 1,200,000 240,000 72,000 20% 64,000,000 32,000,000 3,800,000 1,200,000 510,000 Severe 30% 96,000,000 48,000,000 5,800,000 1,700,000 770,000 Very 20% 64,000,000 32,000,000 7,700,000 2,300,000 1,300,000 Severe 30% 96,000,000 48,000,000 11,500,000 3,500,000 1,930,000 a Adapted from Reed C, Biggerstaff M, Finelli L, Koonin LM, Beauvais D, Uzicanin A, Plummer A, Bresee J, Redd SC, Jernigan DB. Novel framework for assessing epidemiologic effects of influenza epidemics and pandemics. Emerg Inf Dis 2013; 19:85-91. b 2015 US Population estimate used for calculation. 44
 Pandemic Influenza Plan Page 43 Page 45
Pandemic Influenza Plan Page 43 Page 45